In today’s digital landscape, the success of a product often hinges on its UI/UX Design. While these terms are frequently used interchangeably, they encompass distinct elements that are crucial for creating intuitive and engaging digital products. This article will delve into the principles of User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX) design, offering insights into how these disciplines work together to enhance user interaction and satisfaction.
Table of Contents
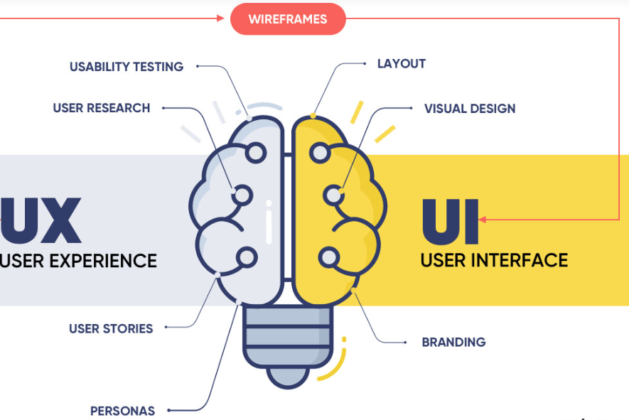
Understanding UI and UX
What is UI Design?
User Interface (UI) design focuses on the visual aspects of a product—the layout, colors, typography, buttons, icons, and overall aesthetic. It’s about creating an interface that is not only visually appealing but also functional. A well-designed UI ensures that users can navigate the product intuitively and accomplish their tasks without frustration.
What is UX Design?
User Experience (UX) design, on the other hand, is broader in scope. It encompasses all aspects of a user’s interaction with a product, including usability, accessibility, and the overall experience a user has. UX design is about understanding the user’s journey and ensuring that every touchpoint is positive and engaging. It involves research, user testing, and feedback to create a seamless experience that meets user needs.
Key Principles of User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX) Design
To create effective User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX) designs, it’s essential to adhere to certain principles that guide the process. Here are some fundamental principles to consider:
1. User-Centric Design
At the core of both UI and UX design is the principle of user-centricity. Designers must prioritize the needs, preferences, and behaviors of users throughout the design process. This involves conducting user research, creating personas, and understanding the context in which users will interact with the product. The ultimate goal is to create solutions that resonate with the target audience.
2. Consistency
Consistency in design helps users build familiarity and confidence in a product. This means maintaining uniformity in visual elements (like buttons and icons) and interaction patterns across the platform. A consistent design language not only enhances aesthetic appeal but also aids usability, as users can predict how different elements will behave based on previous interactions.
3. Visual Hierarchy
Effective UI design employs visual hierarchy to guide users’ attention and help them navigate the interface effortlessly. By strategically using size, color, contrast, and spacing, designers can prioritize information and create a clear pathway for users to follow. This ensures that critical information is easily accessible while less important elements are visually subordinate.
4. Feedback and Response
Providing feedback is essential in UI/UX design. Users should receive clear, immediate responses to their actions—whether it’s a visual change when a button is clicked or a message confirming that an action has been completed. This feedback loop reassures users that the system is responsive and enhances their overall experience.
5. Accessibility
Designing for accessibility is not just a legal obligation; it’s a moral imperative. A good UI/UX design should accommodate users of all abilities and disabilities. This involves using readable fonts, ensuring sufficient color contrast, providing alternative text for images, and making sure that the interface can be navigated using a keyboard. Accessibility broadens the user base and enhances the product’s usability for everyone.
6. Simplification
Simplicity is a guiding principle in both UI and UX design. A cluttered interface can overwhelm users and lead to confusion. Designers should strive to simplify the user experience by minimizing distractions, reducing unnecessary steps in processes, and ensuring that the interface is clean and easy to understand. Less is often more when it comes to design.
7. Usability Testing
No design is perfect from the start. Usability testing is a crucial step in the design process, allowing designers to gather feedback from real users. By observing how users interact with a product, designers can identify pain points and areas for improvement. Iterating on the design based on this feedback helps create a more refined and user-friendly product.
The Intersection of UI and UX
While UI and UX are distinct disciplines, they are inherently connected. A beautiful interface (UI) can fail if it doesn’t provide a satisfying experience (UX), and a great user experience can be undermined by a poorly designed interface. Effective UI/UX design involves a collaborative approach, where visual design enhances the overall user journey, and user feedback informs design choices.
Conclusion
Creating intuitive and engaging digital products requires a deep understanding of both UI and UX design principles. By prioritizing user needs, ensuring consistency, providing clear feedback, and conducting usability testing, designers can craft experiences that not only meet but exceed user expectations. As technology continues to evolve, the importance of thoughtful UI/UX design will only grow, making it an essential area of focus for any digital product team. Whether you’re designing an app, a website, or any other digital interface, embracing these principles will help you create products that users love to engage with.




Your articles never fail to captivate me. Each one is a testament to your expertise and dedication to your craft. Thank you for sharing your wisdom with the world.