In recent years, genetic editing has moved from the realm of science fiction to a revolutionary reality, thanks to breakthroughs like CRISPR. This powerful technology has the potential to transform medicine in ways that were once unimaginable, from curing genetic diseases to tackling cancer and even personalizing medical treatments. In this article, we’ll explore what CRISPR is, how it works, and the groundbreaking ways it’s shaping the future of medicine. Whether you’re a science enthusiast or just curious about the potential of genetic editing, this journey into the future of healthcare promises to be both insightful and exciting.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Imagine if we could “edit” human DNA like we edit text on a Word document. Messed up a word? No problem, just delete it and type something better. While that may sound like sci-fi, this is the incredible promise of CRISPR—a groundbreaking genetic editing technology that’s shaking up the world of medicine. And this isn’t some distant dream of the future—it’s happening now.
In this article, we’ll dive into the fascinating world of CRISPR and beyond, exploring how genetic editing is transforming medicine, from curing genetic diseases to potentially eradicating cancer. Buckle up, because this journey into the future of healthcare is both mind-blowing and a bit of a thrill ride!
What is CRISPR? A Quick Primer
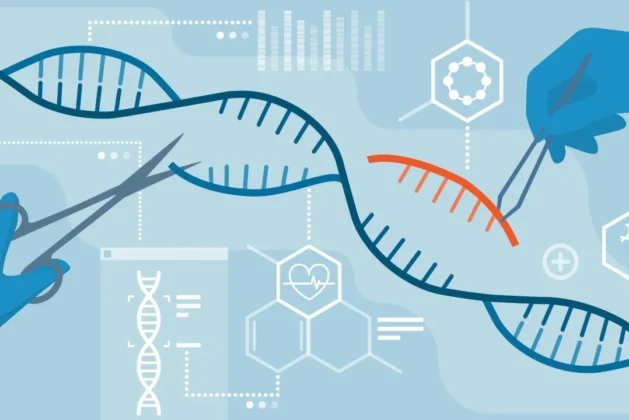
Let’s start with the basics. CRISPR stands for Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats—quite the mouthful, right? But you don’t need to memorize that name to understand the magic behind it. CRISPR is essentially a powerful tool used to “cut and paste” DNA with precision. It’s like the “Find and Replace” feature on your computer, but for genetic code.
Discovered in 2012, this tool works by targeting specific genes in the DNA and either modifying or “editing” them. It has revolutionized the field of genetic research because it’s simpler, faster, and more affordable than previous methods. Scientists are using CRISPR to edit genes in living organisms—including humans—with the aim of treating or even curing genetic diseases.
How Does CRISPR Work?
Picture a pair of molecular scissors. These scissors are guided by a little RNA molecule that knows exactly where to go in the DNA code. Once the scissors arrive at the target gene, they make a cut. The cell then “repairs” the cut by either adding a new piece of DNA or deleting the faulty one. It’s like fixing a typo in a sentence, but on a genetic level.
This ability to edit genes with such accuracy means that we can potentially fix the mutations responsible for genetic disorders. And that’s just the beginning!
CRISPR’s Role in Medicine: A Game-Changer
The potential applications of CRISPR in medicine are vast. Let’s take a look at some of the ways this technology is already changing healthcare, or as we like to call it—making doctors feel like they have superpowers.
1. Curing Genetic Diseases
Imagine being born with a genetic disorder like sickle cell anemia or cystic fibrosis—conditions caused by a tiny mutation in your DNA. With CRISPR, scientists can now correct these mutations at the root cause. It’s like hitting “reset” on your genes to make them function properly.
In clinical trials, researchers have used CRISPR to edit the DNA of patients suffering from sickle cell anemia, and the results have been nothing short of remarkable. Patients are showing signs of recovery, with some even going into remission. In short, CRISPR might just be the tool that brings an end to certain inherited diseases.
2. Tackling Cancer
CRISPR isn’t just about fixing genetic disorders—it’s also showing promise in the fight against cancer. One of the major hurdles in cancer treatment is that tumors are constantly evolving, making them difficult to target. But CRISPR can be used to “program” the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells more effectively.
Researchers are using CRISPR to enhance immune cells (like T-cells) and turn them into cancer-fighting machines. It’s like giving the immune system a superhero upgrade! Early-stage trials are already showing some exciting results in fighting cancers like leukemia and lymphoma.
3. Gene Therapy: Personalized Medicine
One of the most exciting possibilities of CRISPR is personalized medicine. By editing the genes of individual patients, doctors could tailor treatments that are unique to each person’s genetic makeup. Think of it as customizing a treatment plan based on your genetic profile—basically, the medical equivalent of having your own personal health concierge.
This approach could be particularly useful in treating conditions like heart disease, diabetes, or neurological disorders, where treatments can be unpredictable and often involve trial and error. CRISPR could help doctors create more effective and targeted treatments for each individual, ensuring better outcomes.
4. Eradicating Genetic Diseases Before Birth
What if we could prevent genetic diseases before a baby is even born? While we’re not quite there yet, CRISPR has the potential to alter the DNA of embryos, potentially eradicating inherited diseases like Huntington’s disease or Down syndrome before a child is even conceived.
Of course, this raises a lot of ethical questions—should we be editing the genes of embryos? But the potential for eliminating life-altering diseases before birth is undeniably powerful. It’s a delicate topic, but one that will surely continue to dominate discussions in the coming years.
Beyond CRISPR: The Next Frontier in Genetic Editing
While CRISPR is a game-changer, it’s not the only tool in the genetic editing toolbox. Researchers are working on new, advanced technologies that could take genetic editing to even greater heights. Let’s take a quick peek at what lies beyond CRISPR.
1. Prime Editing: The Precision Engineer
Think of prime editing as the precision laser cutter of genetic editing. It’s newer than CRISPR, and it offers even more accuracy when it comes to editing DNA. It has the potential to correct almost any genetic mutation, making it a promising tool for treating diseases that CRISPR can’t fix just yet.
2. Base Editing: A Fine-Tuned Approach
Base editing is another breakthrough that allows scientists to make specific changes to individual DNA bases (the building blocks of genetic code) without making double-stranded breaks. This could prove especially useful for diseases caused by point mutations, where just a single “letter” of DNA needs to be swapped out.
The Ethical Debate: Editing Human Genes
With great power comes great responsibility. And genetic editing, especially in humans, comes with a host of ethical considerations. Should we edit the genes of embryos to prevent diseases, or is that crossing a line? What about editing genes for non-medical purposes, like enhancing intelligence or physical traits?
While these ethical debates are important, the medical potential of CRISPR and other genetic editing tools is undeniable. Scientists and ethicists alike are working hard to find the right balance between innovation and responsibility. But one thing is clear: genetic editing is here to stay, and it’s going to change the way we think about medicine.
Conclusion: A Future of Endless Possibilities
CRISPR and other genetic editing technologies are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in medicine. From curing genetic diseases to enhancing cancer therapies and creating personalized treatments, the potential is limitless. While we still have some ethical and technical challenges to navigate, the future of genetic editing looks incredibly promising.
So, next time you hear someone mention CRISPR, just know that it’s not some futuristic science project—it’s real, it’s happening now, and it’s setting the stage for a healthier, more genetically-advanced world. And who knows? Maybe one day, we’ll all be able to get our genes “edited” like a document in need of a little proofreading. How’s that for progress?
Final Thought: CRISPR may not be a magic wand (yet), but it’s pretty darn close. The future of medicine is here, and it’s genetically edited!
Read More: Gemini AI: The Game-Changer Revolutionizing the World of Technology




For Best Online Courses and Certifications visit https://academylyft.com/
Fantastic site A lot of helpful info here Im sending it to some buddies ans additionally sharing in delicious And naturally thanks on your sweat
Your blog is a testament to your dedication to your craft. Your commitment to excellence is evident in every aspect of your writing. Thank you for being such a positive influence in the online community.