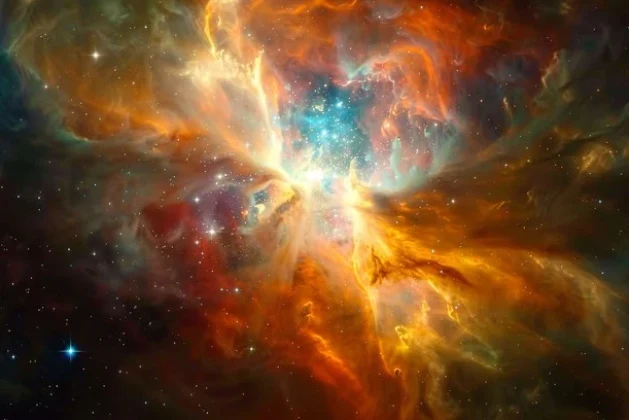
Have you ever looked up at the night sky and wondered where stars come from? Before stars shine brightly in the sky, they begin their lives in vast, colorful clouds of gas and dust called nebulae. These mysterious regions are not just beautiful—they’re essential to the creation of the universe as we know it. Let’s take a closer look at how nebulae work, why they matter, and what role they play in the incredible life cycle of stars.
Introduction: A Star Is Born
When we think about stars, we often imagine their glowing presence in the sky. But every star has a beginning—and that beginning is hidden inside a nebula. These cosmic clouds are where the building blocks of stars, planets, and even life itself originate. Studying nebulae helps us understand how the universe evolves, and how everything around us, including ourselves, is connected to the stars.
Table of Contents
What Exactly Is a Nebula?
A nebula (plural: nebulae) is a massive cloud of gas (mostly hydrogen and helium) and dust floating in space. Some are light-years across and can contain enough material to form thousands of stars. They’re often found in galaxies and are commonly associated with star-forming regions.
Depending on their composition and the stage of stellar development, they can take on different forms and purposes. Some glow brightly due to the energy of nearby stars, while others are dark and cold, waiting for stars to ignite within them.
Types of Nebulae
There are several different kinds, each playing a unique role in the cosmic cycle:
1. Emission Nebula
- Glows due to ionized gases, especially hydrogen.
- Often found in star-forming regions.
- Example: Orion Nebula (M42).
2. Reflection Nebula
- Reflects the light of nearby stars.
- Usually appears blue because shorter blue wavelengths scatter more easily.
- Example: The Pleiades Nebula.
3. Dark Nebula
- Dense clouds that block light from stars behind them.
- Cold, dust-filled regions where new stars begin to form.
- Example: Horsehead Nebula.
4. Planetary Nebula
- Formed from dying stars (not actual planets).
- Often spherical shells of gas ejected by red giants.
- Example: Ring Nebula.
5. Supernova Remnants
- The leftover material after a massive star explodes.
- Highly energetic, often leading to new star formation.
- Example: Crab Nebula.
Nebulae: The Stellar Nurseries
Nebulae are often called stellar nurseries because they are the places where stars are born. Here’s how the process works:
- Gravity Pulls In Gas and Dust: Over time, parts of a nebula begin to collapse under their own gravity.
- Formation of a Protostar: As the cloud condenses, it forms a hot, dense core called a protostar.
- Ignition of Nuclear Fusion: When the core becomes hot enough, hydrogen atoms fuse into helium—this releases massive energy.
- A New Star Is Born: Once nuclear fusion begins, the protostar becomes a fully-fledged main sequence star.
This process can take millions of years, but it’s happening all across the universe, even as you read this article.
Why Are They So Colorful?
One of the most fascinating things about nebulae is their breathtaking appearance. The colors we see in photos are often captured using special filters that detect specific elements like hydrogen (red), oxygen (blue-green), and sulfur (deep red). These images are then colorized to highlight structures we can’t see with the naked eye. Some colors are true to life, while others are enhanced for scientific clarity and visual beauty.
Why Nebulae Matter to Us
You might be wondering—why should we care about some far-off cloud in space? Here’s why:
- Origin of Elements: Many of the elements that make up your body—like carbon, oxygen, and iron—were formed in stars that once emerged from nebulae.
- Understanding the Universe: By studying nebulae, astronomers can learn about how galaxies evolve, how stars form and die, and how planets like Earth come into existence.
- Perspective: Nebulae remind us that everything is connected. The atoms in your body may have once been part of a distant star, born in a nebula billions of years ago.
Final Thoughts: The Majesty of Nebulae
They aren’t just pretty pictures from telescopes—they are cosmic engines of creation. From the smallest dust particles to the mightiest stars, the story of the universe begins inside these vibrant clouds. As we explore more of the universe, they continue to be some of the most exciting and enlightening subjects in astronomy.
Read More: Cardiovascular Health: Everyday Habits That Strengthen Your Circulatory System Naturally